Robot
Frequently asked questions on the robot
I cannot connect my robot to the network with an ethernet cable
WiFi connection
On your first connection to a network, the simpliest is to connect your robot with an ethernet cable.
If you cannot do so:
Use the appropriate cable and connect your computer directly to Reachy 2’s computer. The cable has to be plugged in port (b) of Reachy 2’s hardware interface.
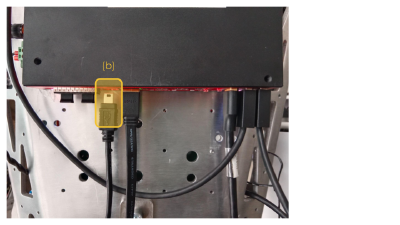
We use tiofor the serial connection. If you haven’t installed it yet on your computer:
apt install tio
>>> groupsIf it doesn't appear in the list, add it with:
>>> sudo usermod -aG dialout $USERThen reboot your computer for the new group to be effective.
Then, in a terminal on your computer, get access to the robot with:
tio /dev/ttyUSB0
Note that the connection could be on another USB port. Check all ports with
ls /dev/ttyUSB*
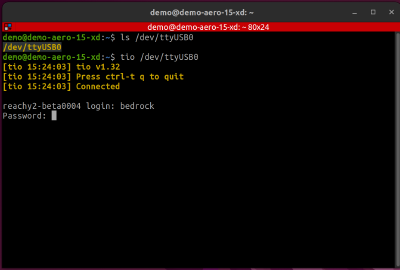
Password: root
Manually connect the robot to a WiFi with:
nmcli device wifi connect <wifi.name> password <your.password>
For example, with the wifi POLLEN-WIFI, with password superstrongpassword:
nmcli device wifi connect POLLEN-WIFI password superstrongpassword
How to connect to my robot
There are several ways to connect to your robot.
SSH connection
Using the robot’s IP address (check Find Reachy 2’s IP if you don’t know it), you can directly connect via ssh to Reachy 2’s computer:
ssh bedrock@<Reachy.2.IP.address>
For example, with robot’s IP being 192.168.1.42:
ssh bedrock@192.168.1.42
Avahi connection
Find the serial number of your robot on its back, connect your computer on the same network as your robot, open a terminal and type:
ping <robot.serial.number>.local
For example, if the serial number is reachy2-beta1:
ping reachy2-beta1.local
Hard-wired connection
Use the appropriate cable and connect your computer directly to Reachy 2’s computer. The cable has to be plugged in port (b) of Reachy 2’s hardware interface.
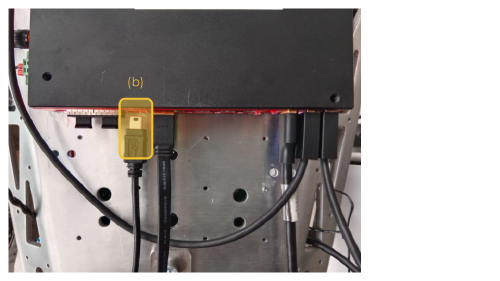
We use tiofor the serial connection. If you haven’t installed it yet on your computer:
apt install tio
>>> groupsIf it doesn't appear in the list, add it with:
>>> sudo usermod -aG dialout $USERThen reboot your computer for the new group to be effective.
Once connected, open a terminal on your computer and run:
tio /dev/ttyUSB0
Note that depending on the elements you connected to the robot, the port could be something else than ttyUSB0. Check other available serial ports with ls /dev/ttyUSB*
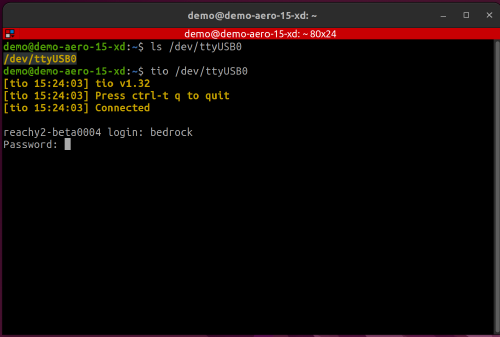
Password: root
You are then connected to Reachy 2 computer!
I want to modify the sound volume
Sound volume
If you want to change the volume, especially for the starting sound of your robot or the output sound when you teleoperate, you need to go on a terminal when the webRTC service is running :
Run:
$ ssh bedrock@your_robot_ip #password : root
$ docker exec -it webrtc_streaming_playback_ros bash
$ alsamixer -c 1
Then, you can set the volume as you wish.
Problems with the motors
Check all logs of the service with:
journalctl -b -u reachy2-core
Problems with the sound or cameras
Check all logs of the service with:
If you are using the cameras with the Python SDK, the cameras are managed by the reachy2-core service.
Check all logs of the service with:
journalctl -b -u reachy2-core
If you are using the teleoperation app, then check:
journalctl -b -u webrtc